It is evident that quick and consequent quarantine zones were a critical success factor. But how did the Chinese healthcare system deal with the crisis? As we will see, digital health solutions played a significant role in containing the virus.
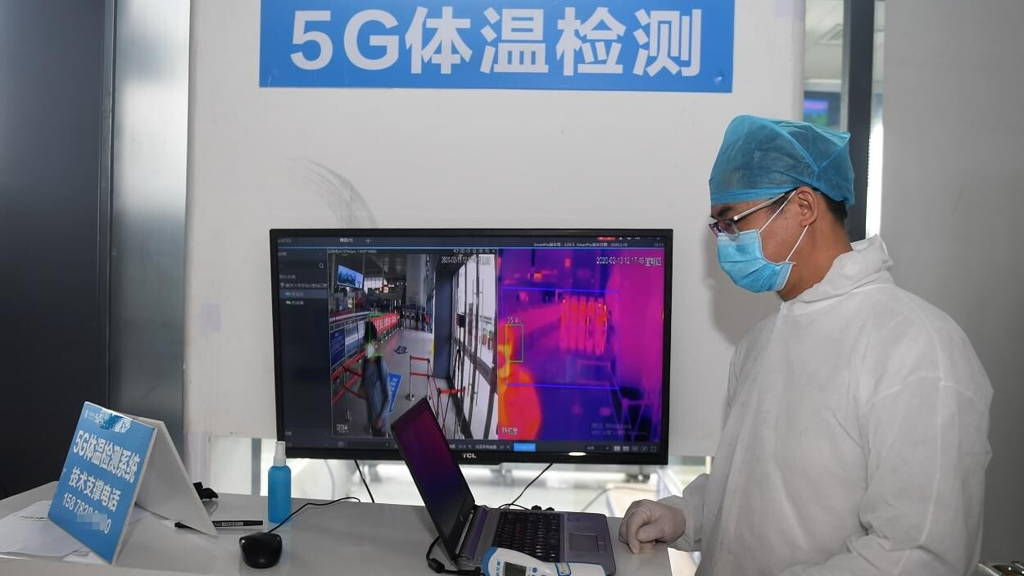
5G is a key technology that enables China’s healthcare to deal with the virus effectively. The West China Hospital of Sichuan University was the first to install a 5G network that allows 25,000 people to communicate with each other simultaneously. It enables a broad scale telehealth system for remote diagnosis of COVID-19. This reduces the possibility of doctors being infected without lowering the speed or quality of care. The technology also solves the severe GP shortage enabling specialists to treat a large number of patients with minimal travel times in different locations. Especially for the people in rural areas that are affected, such digital services improve access to adequate diagnostics significantly and increase the response time to new infections outside of the epicenters, which supports the containment of the virus.
Telemedicine consultations
Similarly, teleconsultation services enable diagnostics with minimal exposure to doctors. Their usage has significantly increased since COVID-19 has emerged. The commercial platform JD Health and AliHealth demonstrated solidarity by offering their basic services for free shortly after the outbreak, contributing to the detection of potential cases in the epicenters. China’s National Health Commission has emphasized the need for the rapid development of more advanced digital consultation platforms to reduce pressure on health institutions. Robotics technologies also mitigate infection risk. Use cases in China have been reported for food delivery to patients in hospitals and the disinfection of contaminated areas.
Teleconsultation services enable diagnostics with minimal exposure to doctors
Monitoring the situation is vital to contain the outbreak – but inherently difficult to do in a country with a dense population as China has. The government has provided a digital solution here via the epidemiology monitoring network “Alipay Health Code.” Leveraging big data analytics enables the system to draw automated conclusions on an individual’s contagion risk and assigns and communicates the results to the platform users via color code visualization. This elegant solution helps to monitor and prevent infections at the same time.
Continuous monitoring
Wearables are another digital health technology that supports monitoring and infection risk reduction simultaneously. The Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center uses a continuous temperature sensor on patients to contain the spread of the virus by detecting symptoms as early as possible while keeping the contact between patients at doctors at a minimal level. The sensors are planned to be extended to monitor heart and respiratory systems to get a more fine-grained picture of a patient’s status.
The crucial question looking forward is: How do we benefit from the COVID-19? As the collective global community, we have to face the epidemic challenges together. At the same time, we have to address the known deficiencies constructively.
Three areas that China needs to improve for better readiness for the next viral threat
- transparent communication, coordination, and monitoring;
- robust health care system with more trained staff;
- enhance the overall healthy behavior of its people.
While the current coronavirus outbreak has become a pandemic, we need to learn from this outbreak and take enormous efforts to overcome the gaps and hopefully, we can then say: next time we are ready.